Glossary of Motor Terms
Time constant
Electrical time constant , Mechanical time constant, Thermal time constant
When there is only one time constant in a certain system, it is the time taken to reach 63% of the next state by giving a change command to a certain steady state. When a constant voltage V is applied to the series circuit of R and L, the current finally becomes V/R, but the time taken to reach 63% is L/R, which is called the electrical time constant. When a constant voltage (V) is applied to the series circuit of R and C, the current initially becomes V/R, but finally it becomes 0. In this case, the time taken for the current to drop to V/R × (1-0.639) = 0.37V/R is equal to CR with the time constant. The rotor of the DC motor is similar in function to a capacitor, and the equivalent electrostatic capacitance (C) is J/KE2. Therefore, the time constant is RJ/ KE2 and this is called the mechanical time constant.
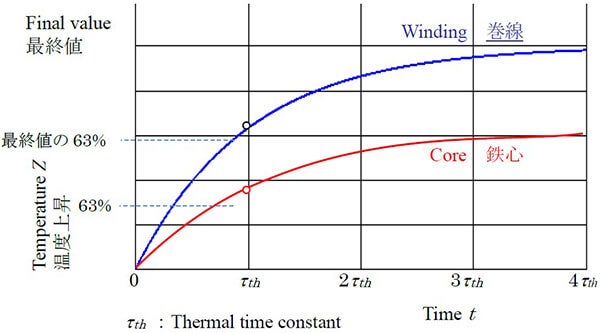
When the motor is started and the rated operation begins, the temperature of the winding and iron core increases exponentially. The time to reach 63% of the final value is called the thermal time constant as shown below.