Glossary of Motor Terms
Equation of motion
This is a basic differential equation for computing the rotational speed of an electric motor and its load. For a structure such as that shown in the figure below, it is written as follows:

Here, J is the sum of the moment of inertia of the rotor and the screw, and the equivalent moment of inertia due to the mass of the table. T is the torque generated by the motor, and is calculated from motor parameters, power supply voltage, inverter, controller and position sensor information. Therefore, the equation of motion becomes a simultaneous differential equation.
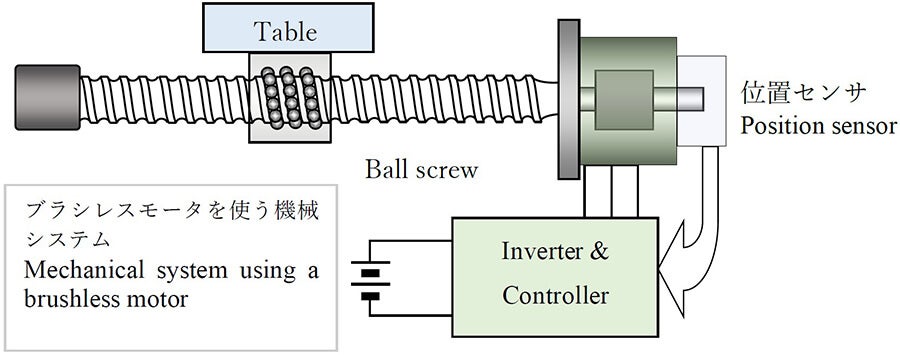
One can call this equation a dynamic equation, but this term is often used for a more general case that includes various time-varying phenomena and effects.
