Implemented Solutions
Next-Generation Motor Control Technology
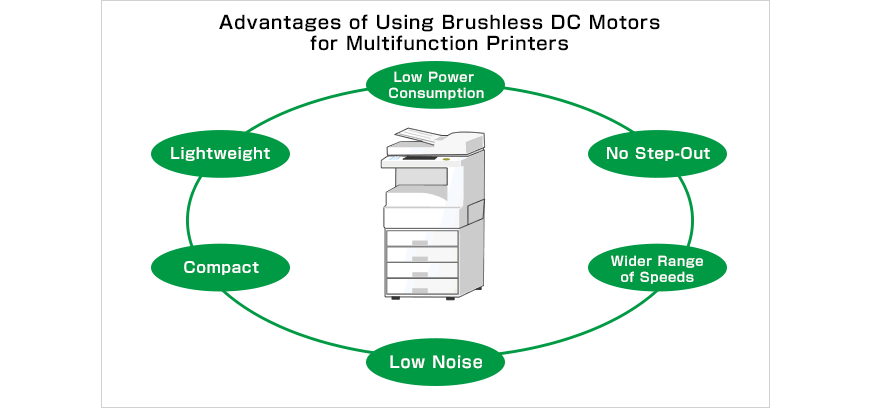
Brushless DC Motors with Position Control Rivaling that of HB Stepper Motors Pave the Way for More Efficient, Lightweight and Compact Products
- NEEDS
- Improving the efficiency of HB stepper motors currently in use
- SOLUTION
- A combination of conventional brushless DC motors and next-generation control technology
Developing Next-Generation Control Technology that Enables High-Precision Position Control
For a long time, HB stepper motors have been the go-to solution for applications that require accurate position control, such as transporting sheets of paper inside multifunction printers or bills inside ATMs. However, in recent years, demand for more compact and energy efficient products has increased. In order to meet these needs, we have combined our brushless DC motors—the mainstay of our business—with next-generation control technology, resulting in small and efficient brushless DC motors with position control rivaling that of HB stepper motors in terms of precision. These brushless DC motors are capable of rotating incrementally and holding discrete positions in the same way as HB stepper motors.

Large multifunction printers, for example, usually contain 10 or more HB stepper motors. Since brushless DC motors differ from HB stepper motors in terms of drive method and position-control precision, brushless DC motors have, up until now, been unable to fulfill the basic characteristics required for this particular application, even though the demand for their efficiency and compactness has been present all along. However, this changed with the advent of next-generation control technology; brushless DC motors are now capable of fulfilling the needs of the market, bringing a wealth of benefits to multifunction printers.
The Process that Led to the Development of the Next Generation of Motor Control Technology
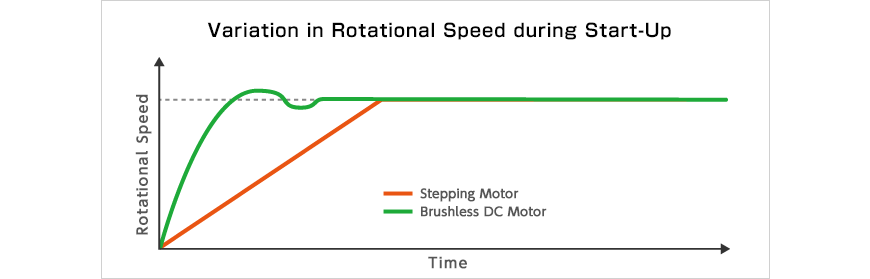
In contrast with HB stepper motors that control the rotation angle by responding to input pulses, brushless DC motors converge to specified positions in an undulating manner while operating on power supplies that are constantly on. In order to be able to use brushless DC motors in place of HB stepper motors two major challenges had to be overcome: improving the precision of the position-control function and reducing the variation in speed during start-up. The former issue was addressed through development of new high-precision optical encoders and control methods, while the latter problem was overcome through application of quality engineering—optimization of parameters based on analysis of control factors. As a result, we managed to match the properties of the brushless DC motors with those of HB stepper motors.
Brushless DC motors accelerate as fast as possible within the limitations imposed by the electric current until they exceed the target rotational speed and start decelerating instead. This acceleration-deceleration process is repeated, in a manner resembling a damped sine wave, until the motor attains the desired speed. The new control methods developed by Nidec minimizes this fluctuation and allows for rapid acceleration and deceleration, introducing new functionality such as reducing the time required to print the first page of a document.
Future Outlook
In addition to multifunction printers, we are currently proposing similar brushless DC motor-based solutions—tailored to meet the needs our customers—in other areas where HB stepper motors are used widely, including ATMs, robots, conveyor belts, surveillance cameras and more. Recently, our internal software development team has succeeded in developing intelligent next-generation motors with fully software-based control. By improving brushless DC motors' responsiveness to control we expand their areas of application to include advanced office equipment, home appliances, service robots and more while contributing to a sustainable and convenient society.
