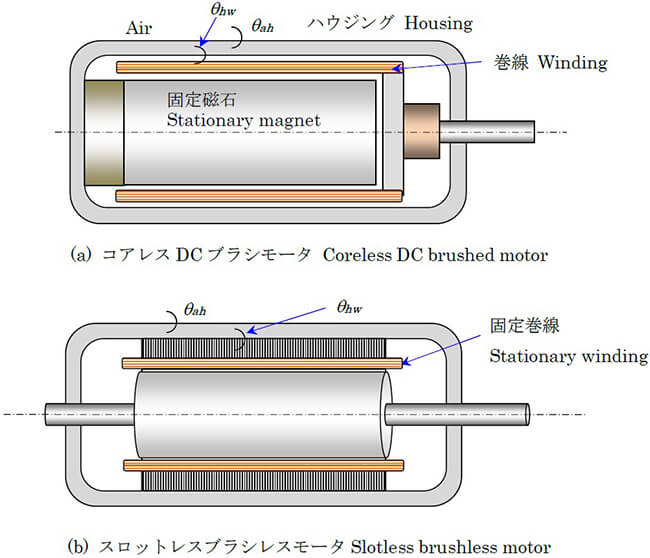
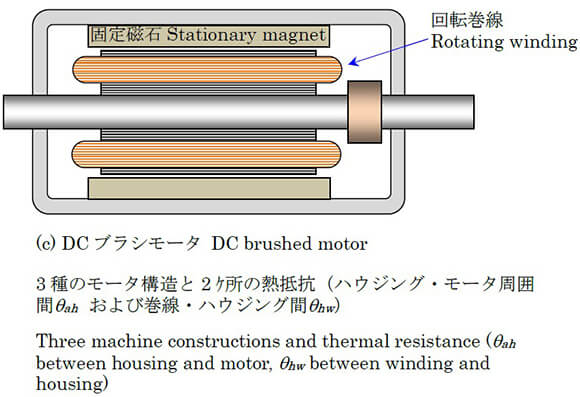
Glossary of Motor Terms
Thermal resistance
The relationship between the heat generated in the motor, particularly the winding, and the surrounding temperature is expressed using a coefficient known as thermal resistance, here denoted Θ. We assume that heat is first transferred from the winding to the housing. When thermal equilibrium has been attained, assuming that the difference of the temperatures of the winding and housing, denoted Zw and Zh respectively, is proportional to the amount of heat generated per second P (i.e., thermal loss in the winding, units in W), we have
Zw-Zh=ΘwhP
The heat is then released from the housing to the surrounding air, which can be expressed using the thermal resistance Θha between the housing and surrounding air and denoting the ambient temperature by Za, as follows.
Zh-Za=ΘhaP
Combining the two expressions, the relation between the winding temperature and ambient temperature is obtained as follows.
Zw-Za=(Θwh+Θha)P or Z=(Θwh+Θhb)P+Za
where
Θha=thermal resistance between the housing and surrounding
air or oil (liquid)
Θwh=thermal resistance between the winding and housing