Glossary of Motor Terms
Switched reluctance motor
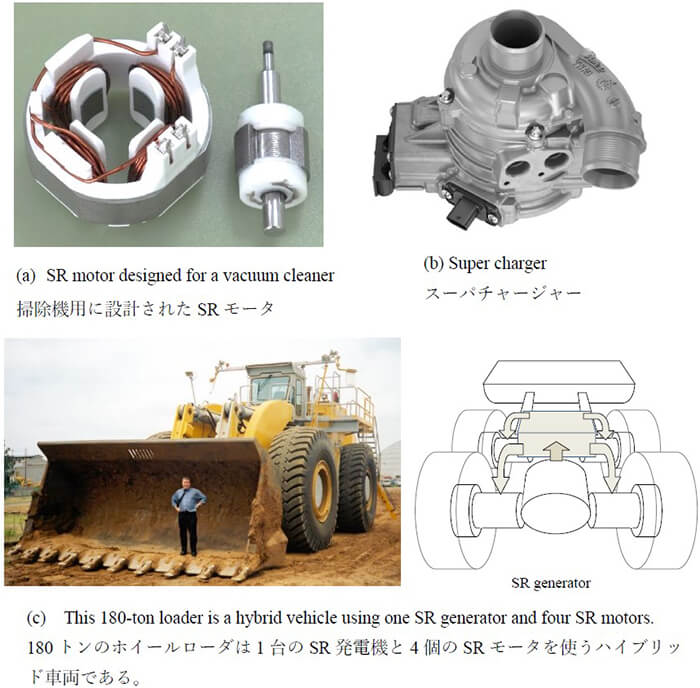
The stator and rotor cores both have salient poles; that of the stator carries concentrated windings, but the rotor has neither windings nor permanent magnets. This operates as a brushless motor. The simplest structure that takes advantage of the feature that enables high-speed operation is a two-phase winding, as shown in photo (a), where the rotor has only two salient poles.
As seen in fig. (c). The primary use of the SR motor is in heavy-duty industrial electric vehicles.
Term List (S)
- Salient-pole torque
- Salient-pole rotor-stator
- Sensorless drive
- Separately-excited DC motor
- Shaft, shapes of
- Simulation
- Sinusoidal voltage
- Skew,Skewed slots
- Slip ring
- Slot liner
- Slotless rotor
- Slot-pole combination
- Slots and teeth
- Small electrical motor
- Solenoid
- Space factor, Slot fill factor
- Speed control
- Speed variation rate
- Spindle motor
- Squirrel cage rotor
- Squirrel-cage induction motor
- Stall torque
- Starting torque
- Sturgeon's motor
- Switched reluctance motor
- Switched reluctance motor, Early
- Switching elements
- Synchronous speed
