Glossary of Motor Terms
Rotor cross-sectional structures
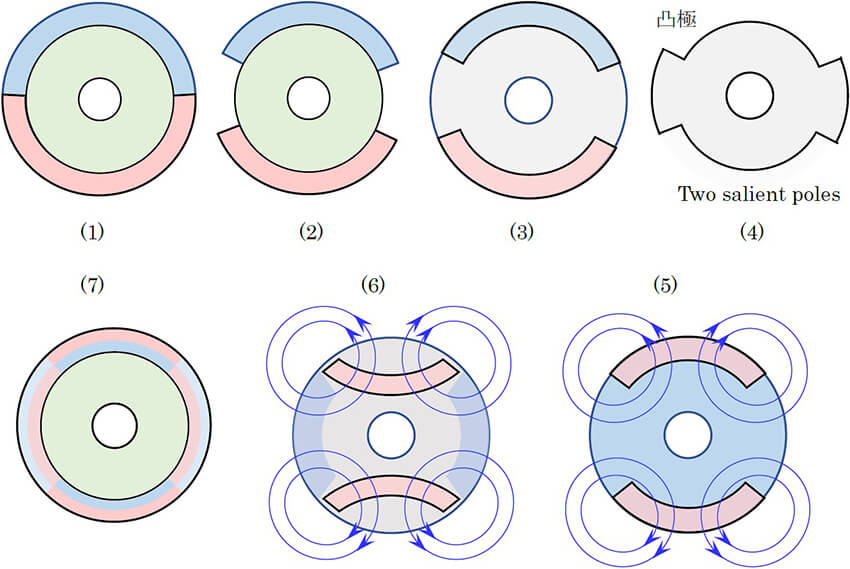
Consider the cross section of a rotor structure using a permanent magnet.
(1) is a cylindrical 2-pole SPM type. It is assumed that one ring-shaped magnet is used and that the lower part
is magnetized to the N pole and the upper part to the S pole.
(2) is a structure using a segment type magnet.
(3) is a structure in which the cross section is circular, including the yoke. This type is rarely actually
used. Removal of the magnet from this will result in
(4), which is a salient pole type and becomes the basic form of an SR motor. In other words, (3) is a
combination of a permanent magnet and a reluctance motor.
(5) is a system that uses two permanent magnets of the same polarity, unlike (3), and it becomes a pseudo four
pole. However, it is combined with a bipolar reluctance motor, so normal performance cannot be expected.
(6), instead, can incorporate a four-pole reluctance-motor structure by embedding a magnet. In other words, in
this structure, the d axis and the q axis of 4 poles are formed and become the object model of vector control.
On the other hand,
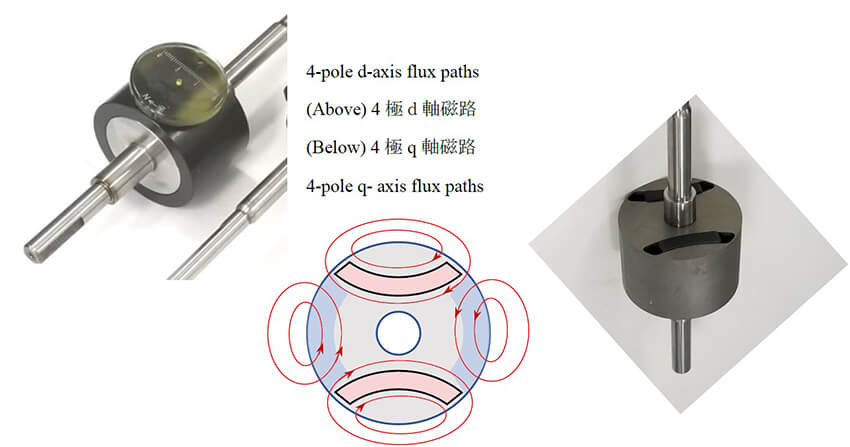
(7) is a four-pole SPM type. The photographs are examples of these two types, and they show contrasting
characteristics.
Term List (R)
- Rare earth magnet
- Reactive power
- Rectification via commutator
- Regenerative brake
- Reluctance motor
- Remanence,Remanent magnetization
- Resolver
- Reversible motor
- Revolutions per minute (rpm)
- Revolutions per second (rps)
- Revolving field (Rotating field)
- Revolving field motor
- Right-hand screw law
- Ring spring
- Riser
- RMS (Root-mean square) value
- Rotor, Stator
- Rotor cross-sectional structures
